Healthy Aging and Maintaining Vitality for Well-being
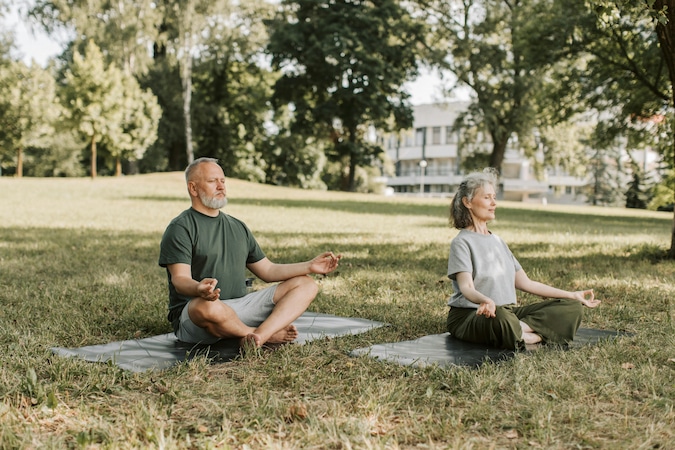

Aging gracefully requires a proactive approach to health. Seniors can maintain vitality and well-being by prioritizing nutrition, exercise, and preventive care. These strategies help reduce the risk of chronic diseases and enhance overall quality of life.
As life expectancy increases, the focus shifts to not just living longer but living better. A well-rounded approach involving proper nutrition, physical activity, and regular health screenings can significantly improve the way we age. Additionally, access to quality health insurance, like that offered by SelfGood, can ensure seniors receive the care they need to stay healthy and vibrant.
Key Takeaways:
- Proper nutrition is essential for maintaining muscle mass and energy levels.
- Regular physical activity improves cardiovascular health, flexibility, and mental well-being.
- Preventive health screenings help detect issues early, promoting long-term vitality.
- Social engagement and mental wellness are critical factors for aging well.
- Sleep, rest, and a safe home environment enhance quality of life for seniors.
The Role of Nutrition in Healthy Aging

Good nutrition is a cornerstone of healthy aging. As we age, our bodies need more specific nutrients to maintain energy, support bone health, and reduce inflammation.
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can help stave off chronic conditions like osteoporosis and heart disease. Key nutrients such as calcium, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids play vital roles in supporting bone strength, brain health, and heart function.
Nutrients Vital for Seniors’ Health
- Calcium and Vitamin D: Essential for bone health, reducing the risk of fractures.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish, these fatty acids help reduce inflammation and support heart health.
- Protein: Critical for muscle preservation, protein can be found in lean meats, beans, and eggs.
- Fiber: Helps with digestion and controls blood sugar levels, found in whole grains and vegetables.
- Antioxidants: Berries and dark leafy greens can help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Eating nutrient-dense foods becomes especially important in older age as appetite can decrease and digestive function may change. Seniors should focus on whole, unprocessed foods, and hydrate regularly to prevent dehydration.
Dietary Concerns for Seniors
As we age, our bodies process food differently. Appetite may decrease, and certain foods may become harder to digest. Here are some common concerns:
- Malnutrition: Seniors may struggle with eating enough food or getting the right nutrients.
- Dehydration: Often, seniors do not feel thirsty as often, leading to dehydration.
- Food Sensitivities: Aging can change how the body reacts to certain foods, requiring dietary adjustments.
A Mediterranean or plant-based diet can offer seniors a balanced, nutrient-dense meal plan. These diets emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, all of which provide the energy and nutrients necessary for healthy aging.
The Importance of Physical Activity for Aging Well
Staying active as you age is vital for preserving physical and mental well-being. Regular exercise supports cardiovascular health, helps maintain muscle mass, improves flexibility, and boosts mood.
Benefits of Regular Exercise for Seniors
Exercise not only strengthens the heart and lungs but also helps keep muscles strong and joints flexible. Regular physical activity can improve balance, reducing the risk of falls—a common concern for seniors.
- Cardiovascular Health: Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling help maintain heart health.
- Muscle Strength: Resistance training or using resistance bands preserves muscle mass, which tends to decline with age.
- Flexibility and Balance: Exercises like yoga or Tai Chi enhance flexibility and balance, reducing fall risk.
Safe and Effective Exercise Routines
When it comes to exercise, seniors should focus on routines that are both safe and effective:
- Strength Training: Use light weights or resistance bands to maintain muscle mass.
- Aerobic Exercise: Activities such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling promote heart health.
- Flexibility and Balance: Yoga or simple stretching can enhance flexibility, while exercises like Tai Chi improve balance.
Overcoming Barriers to Exercise
Mobility issues, arthritis, and fear of injury are common barriers to regular exercise for seniors. However, low-impact exercises, joining fitness communities, and working with trainers can help seniors stay active while minimizing these challenges.
Preventive Health Screenings for Seniors
Preventive care is essential to catching potential health issues early, allowing seniors to take action before a condition worsens.
The Role of Preventive Care in Healthy Aging
Screenings for various health conditions can detect issues in their early stages. Regular checkups for blood pressure, cholesterol, diabetes, and cancer can identify risks early on and lead to more effective treatments.
Key Screenings for Seniors
- Cancer Screenings: Regular screenings for breast, prostate, and colon cancer are crucial.
- Blood Pressure & Cholesterol: Monitoring these helps manage cardiovascular risks.
- Bone Density Tests: Crucial for detecting osteoporosis, which can lead to fractures.
- Vision and Hearing: Regular eye and ear exams can help detect early sensory loss.
Immunizations and Vaccinations
Vaccinations are essential for seniors as the immune system weakens with age. Flu shots, pneumonia vaccines, and shingles vaccines can protect against serious illnesses and complications.
Managing Chronic Conditions and Maintaining Mental Wellness
Aging often comes with chronic conditions, such as diabetes or arthritis. Proper management of these conditions through medication, lifestyle changes, and regular health screenings is essential for a healthy and fulfilling life.
The Link Between Mental Health and Aging
Mental health is a significant part of aging well. Depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline are common in older adults. Staying mentally active by engaging in puzzles, reading, and social interaction can help keep the brain sharp.
Mental wellness and physical health are interconnected, so maintaining good mental health can directly impact overall well-being.
Social Connections and Emotional Well-being
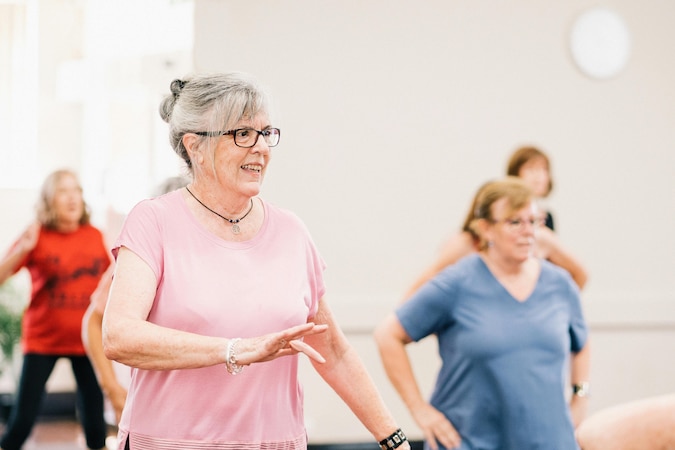

Staying connected with others is crucial for emotional and mental health. Seniors who remain socially active are more likely to experience better mental and physical well-being.
The Importance of Social Engagement
Social connections reduce the risk of loneliness, which is linked to cognitive decline and depression. Seniors can stay engaged by volunteering, joining clubs, or using technology to stay in touch with family and friends.
Cultivating Strong Social Networks
Building and maintaining a strong social network helps seniors stay emotionally healthy. Family, friends, community centers, and even social media can all help foster meaningful connections.
Sleep and Rest for Healthy Aging
Sleep becomes more important as we age, yet many seniors struggle with getting enough rest. Sleep supports physical recovery, boosts memory, and enhances mood.
Common Sleep Challenges
Seniors may experience insomnia, sleep apnea, or changes in sleep patterns. These issues can result from medication side effects, lifestyle changes, or medical conditions.
Tips for Better Sleep
To improve sleep, seniors should establish a consistent bedtime routine, create a restful environment, and avoid caffeine in the evening. Relaxation techniques like meditation or breathing exercises can also improve sleep quality.
Creating a Safe and Healthy Home Environment
A safe living environment is critical for seniors who want to age in place. Home modifications can help prevent falls and other accidents, ensuring independence and comfort.
Home Modifications for Aging in Place
- Grab Bars and Ramps: Installing grab bars in bathrooms and ramps where necessary can enhance safety.
- Lighting and Fall Prevention: Improve lighting and eliminate tripping hazards like loose rugs.
Ergonomic Design for Comfort
Ergonomic furniture and assistive devices such as raised toilet seats or supportive chairs can enhance comfort and safety at home.
Final Thoughts
Aging well is about more than just adding years to your life; it’s about adding life to your years. By focusing on nutrition, regular exercise, preventive care, and mental wellness, seniors can maintain vitality and live fulfilling lives. Proactively taking these steps ensures a higher quality of life and greater independence in the golden years.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most important health screenings for seniors?
Seniors should prioritize cancer screenings, blood pressure and cholesterol checks, and bone density tests to stay ahead of potential health risks.
What types of exercise are safest for aging adults?
Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, yoga, and resistance training are safe and effective for seniors.
How can seniors improve their diet?
Seniors should focus on nutrient-dense foods such as leafy greens, whole grains, lean proteins, and foods rich in calcium, vitamin D, and omega-3s.
Sources:
1. Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Preventive Health Screenings for Older Adults. https://www.mayoclinic.org/
2. National Institute on Aging. (n.d.). Safe Exercises for Seniors. https://www.nia.nih.gov/
3. Oldways. (n.d.). Mediterranean Diet for Seniors. https://www.oldwayspt.org/