Avoiding Fats for Better Health: Practical Tips for a Balanced Lifestyle

Confused by conflicting health advice? You’re not alone. In this article, we’ll focus on one realistic and impactful health tip: reducing saturated and trans fats in your diet. This doesn’t mean eliminating fats altogether—our bodies need healthy fats to function well. Instead, we’ll guide you on how to make smarter choices for a balanced lifestyle.
Here’s what we’ll cover:
- Why it’s important to avoid saturated and trans fats.
- Simple substitutions for healthier meals.
- How to read food labels to spot unhealthy fats.
- Practical, sustainable tips for long-term success.
Why Avoid Saturated and Trans Fats?

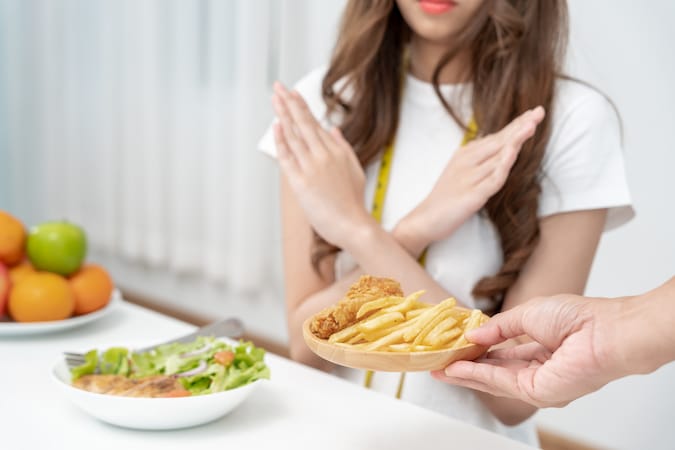
Saturated fats and trans fats are linked to various health issues, including heart disease, high cholesterol, and obesity. While they’re common in processed foods and animal-based products, reducing their intake can significantly benefit your overall health.
Key Reasons to Limit These Fats:
- Heart Health:Saturated and trans fats can increase LDL (bad cholesterol), leading to clogged arteries.
- Weight Management:These fats are calorie-dense and may contribute to unhealthy weight gain.
- Inflammation Reduction:Trans fats, in particular, can trigger inflammation, which is linked to chronic diseases.
For more insights on how to maintain a healthy lifestyle, explore resources at SelfGood .
Simple Substitutions for Healthier Meals
Switching to healthier alternatives doesn’t have to be complicated. Here are some easy swaps to incorporate into your diet:
Healthier Cooking Oils:
- Use:Olive oil, avocado oil, or coconut oil.
- Avoid:Butter, lard, or hydrogenated vegetable oils.
Protein Choices:
- Use:Fish (e.g., salmon or mackerel), skinless poultry, or legumes.
- Avoid:Fatty cuts of red meat or processed meats like sausages.
Snacks and Desserts:
- Use:Nuts, seeds, or fresh fruit.
- Avoid:Packaged cookies, chips, or pastries containing trans fats.
Looking for more health tips? Check out our blog for expert advice on nutrition and wellness.
How to Read Food Labels for Unhealthy Fats
Reading food labels is a simple yet powerful habit to develop. Understanding what to look for can help you make informed choices:
What to Watch For:
- Saturated Fat Content:Aim for less than 10% of your daily calorie intake from saturated fats.
- Trans Fats:Avoid foods with partially hydrogenated oils listed in the ingredients.
- Cholesterol Levels:High cholesterol levels often indicate high saturated fat content.
When dining out, ask for nutritional information or choose dishes with fresh, whole ingredients.
Practical Tips for Long-Term Success
Building sustainable habits is key to reducing saturated and trans fats in your diet. Here are realistic steps you can take:
- Plan Your Meals:Preparing home-cooked meals lets you control the type and amount of fat used.
- Practice Portion Control:Even healthy fats should be consumed in moderation.
- Limit Fast Food:Opt for healthier options when eating out, such as salads or grilled items.
- Stay Consistent:Make small, manageable changes instead of overhauling your diet overnight.
The Role of Health Insurance in Supporting a Balanced Diet
Access to health insurance can help cover preventive care services, including nutrition counseling. If you’re unsure which plan is right for you, explore health insurance options tailored to your needs.